Implantologie
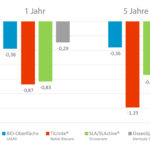
Hoher marginaler Knochenerhalt mit Implantaten BioniQ®
Als sehr wichtiger Faktor, der die Zufriedenheit der Patienten nach der Implantatinsertion beeinflusst, werden gute Funktionsfähigkeit und optimale Ästhetik betrachtet. Eine natürlich aussehende Ästhetik sichert die Stabilität des Alveolarknochens im Einklang mit der physiologischen Dimension der Weichgewebe (biologische Breite). Dies kann nur unter solchen Umständen erreicht werden, wenn das Implantat, die Suprakonstruktion und der Zahnersatz im vollständigen Einklang funktionieren.
Es wurde eine Meta-Analyse1 veröffentlicht, aus der sich ergibt, dass es einen statistisch signifikanten Unterschied zwischen Premium-Implantatoberflächen gibt. Der Vergleich der Meta-Analyse mit den Ergebnissen von Studien der Implantate BioniQ® 2, 3 bestätigt, dass die bioaktive BIO-Oberfläche von den Implantaten BioniQ® den neuesten Trends entspricht und zu den Premium-Marken gehört. Quellen.
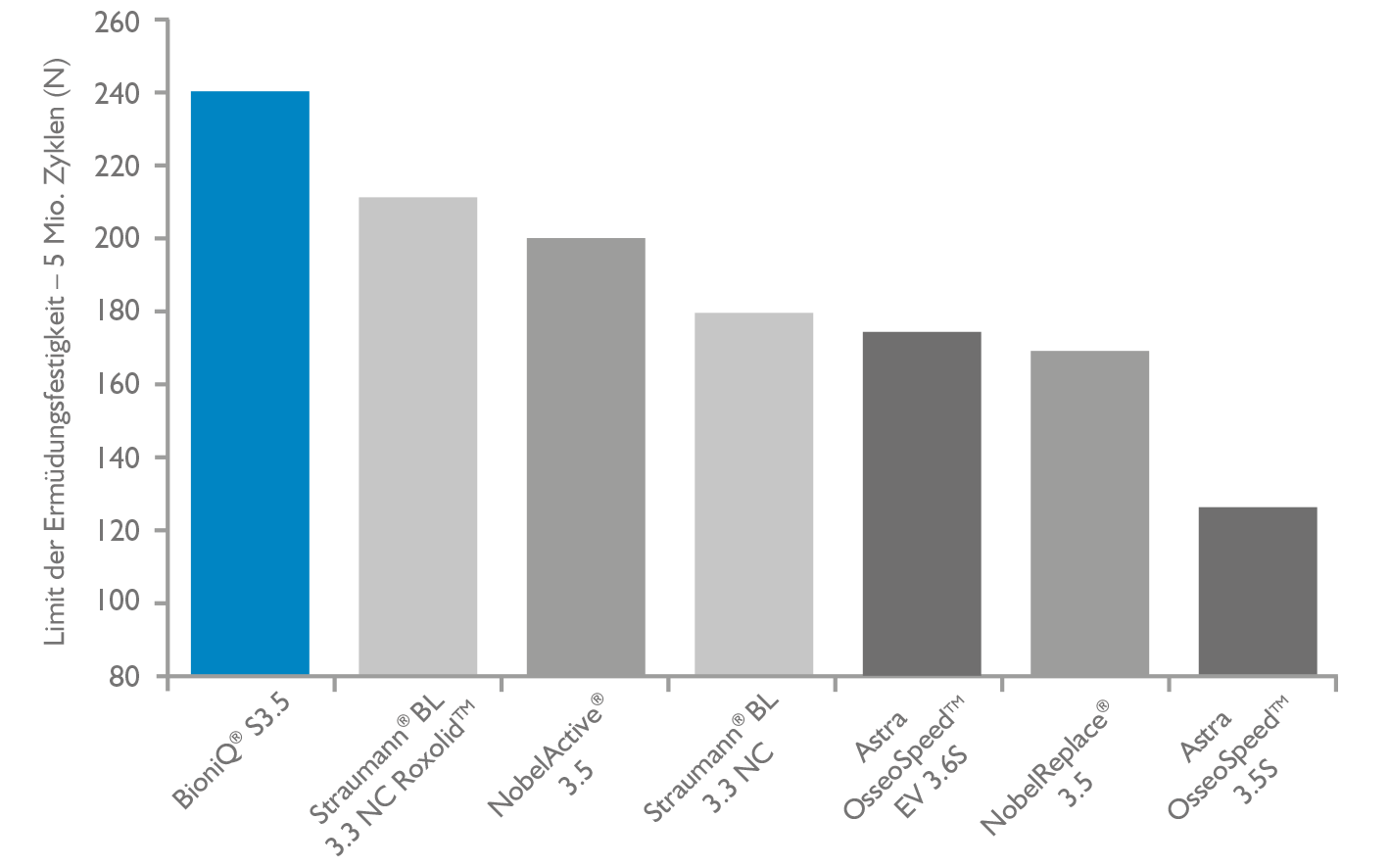
Hohe Festigkeit der Verbindung Implantat-Aufbaupfosten (die unabhängige Vergleichstudie – ISO 14801)
Bei der Festigkeitsprüfung wird die Beanspruchung des Implantates und des Aufbaupfostens durch die Kinematik beim Kauen gemäß ISO 14801 überprüft. Fünf Millionen Kauzyklen, die bei der Prüfung der Dauerfestigkeit der Verbindung von Implantat und Aufbaupfosten simuliert werden, entsprechen ca. 20 Jahren natürlicher Belastung des Implantates im Mund. Quellen.
Fallberichte
- Sammlung der klinischen Fälle gratis herunterladen
Es enthält Fallberichte über das Implantatsystem BioniQ®, das auf Einfachheit und Effektivität basiert. Neununddreißig Implantate sind mit einer prothetischen Plattform zu behandeln. Unsere logisch und sinnvoll angeordnete Kassette mit Minimalanzahl von Instrumenten dient zur chirurgischen sowie prothetischen Behandlung mit allen unseren Implantaten. Die führenden Zahnärzte teilen Ihr Wissen und ihre Erfahrungen in zwölf klinischen Fallberichten.
- Implantatprothetik im atrophierten Ober- und Unterkiefer; Dr. Volker Bonatz, M.Sc., M.Sc.: Implantologie Journal 11/24
In der Implantatprothetik stellt die Behandlung von Patienten mit atrophierten Ober- und Unterkiefern eine komplexe Herausforderung dar. Dr. Volker Bonatz beschreibt die vollständige chirurgisch-prothetische Komplettbehandlung einer Patientin, die mit einer stark atrophierten Kieferanatomie und unzureichenden Restzähnen vorstellig wurde. Die schablonengeführte Pilotbohrung wurde ausgewählt. Aufgrund der Analyse von anatomischen Strukturen wurden die Implantate BioniQ® mit einem Durchmesser von 2,9 mm eingesetzt.
- Implantation bei Teenagern in der ästhetischen Zone; Doc. MUDr. Martin Starosta, Ph.D.: Implantologie Journal 6/2024
Das schöne Lächeln hängt vom ästhetischen Aussehen der Zähne sowie des sichtbaren Gingivabereiches ab. Dr. Martin Starosta beschreibt in seinem Fallbericht die Behandlung einer 18-jährigen Patientin, die in seine Praxis mit Problemen mit dem Zahn 21 aufgrund eines alten Traumas überwiesen wurde. Das Implantatsystem BioniQ® kam zur Anwendung. Durch minimalinvasive chirurgische Eingriffe und die Schonung des umliegenden Gewebes konnte ein bestmögliches ästhetisches und gleichwohl funktionelles Ergebnis erzielt werden.
- Richtige Implantatprothetik für langfristigen Erfolg; Dr. Volker Bonatz M.Sc. M.Sc.: Implantologie Journal 3/2021
Ältere Patienten verlangen die Beibehaltung des Kaukomforts unter minimalinvasiver Behandlung. Nicht selten ist noch ein begrenzter Kostenrahmen vorhanden. Dr. Volker Bonatz M.Sc., M.Sc. ist dieses bewusst. Die hohen Erwartungen seiner Patienten erfüllt er auch dank unseren Implantaten BioniQ® und dem Knochenersatzmaterial PORESORB-TCP.
- Implantate und Prothetik für den alternden Patienten; Dr. Volker Bonatz M.Sc. M.Sc.: Implantologie Journal 9/2021
Die Altersstruktur der Patienten in den zahnärztlichen Praxen verschiebt sich nach oben. Die Erwartungen steigen genauso. Mit welchen Fragen muss sich der implantologisch tätige Zahnarzt auseinandersetzen und wie sind ihm unsere durchmesserreduzierten Implantate BioniQ® Plus von Hilfe.
- Schablonengeführte Chirurgie bei geringem Knochenangebot; Dr. Pavel Hyspler: Implantologie Journal 10/2021
Wenn man aus Sicht der klassischen Implantation an Stellen mit nicht ausreichendem Knochenangebot implantieren möchte, kommen mehrere Möglichkeiten in Frage. Als eine scheint auch Guided Surgery BioniQ® zu sein, wie Dr. Pavel Hyspler in seinem Fachartikel berichtet. Die modernen Technologien ermöglichen, auch in der Nähe anatomisch riskanter Strukturen sicher zu implantieren. So bringen sie dem Patienten mehr Komfort und damit auch höhere Zufriedenheit.
- Mögliche Nutzung von computerassistierten Operationsverfahren. Funktionelle und ästhetische implantologische Behandlung; Dr. Jiri Hrkal: Implantologie Journal 10/2022
Das Ziel einer implantologischen Behandlung ist ein funktionelles, ästhetisches, langfristig stabiles und nachhaltiges Ergebnis. Aufgrund mehrjähriger Erfahrungen mit statischer sowie dynamischer Navigation berichtet Dr. Jiri Hrkal in seinem Fachartikel darüber, wie ihm aktuelle Technologien, Materialien, Verfahren sowie BioniQ® Implantate helfen, dieses Ziel zu erreichen.
Klinische Studien auf Englisch
- The influence of biological width violation on marginal bone resorption dynamics around two-stage dental implants with a moderately rough fixture neck: A prospective clinical and radiographic longitudinal study; Strnad J., Novák Z., Nesvadba R., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Int J Dent & Ora Hea 2021; 7:6, 20-36.
- Marginal bone response of submerged and non-submerged osteoconductive alkali-etched implants in thick and thin biotypes: A 2-year clinical follow-up study; Novák Z., Strnad J., Nesvadba R., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34(5):1184-1194.
- 5-Year Prospective Clinical Study of Early Loaded BioniQ Implants with Bioactive Alkali-Etched Surface. Results after 1-Year of Follow-up; Novák Z., Strnad J., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: LKS, 5/2018: 116–125.
- Influence of abutment height and implant depth position on interproximal peri‐implant bone in sites with thin mucosa: A 1‐year randomized clinical trial; Pico A., Martín-Lancharro P., Caneiro L., Nóvoa L., Batalla P., Blanco J.: Clin Oral Impl Res. 2019;00:1–8.
- Chronological Age as Factor Influencing the Dental Implant Osseointegration in the Jaw Bone; Papež J., Dostálová T., Chleborád K., Kříž P., Strnad J.: Prague Medical Report / Vol. 119 (2018) No. 1, p. 43–51
- Effect of abutment height on interproximal implant bone level in the early healing: A randomized clinical trial; Blanco J., Pico A., Caneiro L., Nóvoa L., Batalla P., Martín-Lancharro P. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2017;00:1–10.
- Development of Implant Stability During Early Healing of Immediately Loaded Implants; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Brázda T., Strnad J., Čapek L., Slezák R.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2012; 27 : 619–627.
- Changes in Stability After Healing of Immediately Loaded Dental Implants; Simunek A., Strnad J., Kopecka D., Brazda T., Pilathadka S., Chauhan R., Slezak R., Capek L.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, Vol. 25, No. 6, 2010, p. 1085–1092.
- Teeth in six hours; Šimůnek A., Vosáhlo T., Kopecká D., Brázda T., Sobotka M., Dufková D.: Implantologie Journal 8/2006.
- Early loading (4 weeks) of dental implants Impladent in maxilla and mandible – monitoring of the healing process using resonance frequency analysis; Štěpánek A., Strnad J., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz Vol. 14, No. 9, 2005.
- Reduced healing time of Impladent implants with bioactive surface; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Strnad J.: Quintessenz Vol. 13, No. 6, 2004.
- Internal sinus augmentation using porous resorbable calcium phosphate ceramic material; Nathanský Z., Strnad J., Veselý P.: Clin. Oral Impl. Res. Vol. 14, No. 4, 2003.
- Replacement of individual teeth with IMPLADENT implants – a 5 year report; Šimůnek A.: Quintessenz, Vol. 7, No. 6, 1998.
- Extention of alveolar ridge without raising the mucoperiosteal flap using minimally-invasive dental implant surgery – a new step in effective implantology; Šmucler R., Barták P.: Implantologie Journal 2/2007.
- Reconstruction of cleft palate using implants – Case Report; Dostalová T., Holakovský J., Bartoňová M., Seydlová M., Smahel Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 16, No. 9, 2007.
- Is Lateral Sinus Lift an Effective and Safe Technique? Contemplations after the performance of one thousand surgeries; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Brázda T., Somanathan R. V.: Implantologie Journal 6/2007.
- Transversal Screw-retained prostheses fixed on dental implants; Podstata J., Kozisek E., Mulicek M.: Implantologie Journal 3/2007.
- Replacement of shortened dental arch using Impladent implants; Šimůnek A.: Quintessenz, Vol. 4, No. 12, 1995.
- Screw-retained prostheses supported by implants; Nathanský Z., Šváb R., Rádlová Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 5, No. 12, 1996.
- A 5-year follow-up study on Impladent Dental Implants; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Krulichová I., Škrabková Z., Mounajjed R.: Quintessenz, Vol. 10, No. 10, 2001.
- Internal sinus floor elevation – new dental implantology possibilities; Nathanský Z.: Čes. Stomat. 103/51, 2003, 6:229-233.
- Stability time dependence of loaded and unloaded dental implants; Šimůnek A., Strnad J., Kopecká D.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. Vol. 16, No. 4, 2005.
- STI-Bio titanium implants with bioactive surface design; Šimůnek A., Strnad J., Novák J., Strnad Z., Kopecká D., Mounajjed R.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. 12, 2001.
- Long-term (9 years) experience with narrow diameter implants (2.9 mm); Podstata J., Hudler T., Novák J., Kožíšek E., Quintessenz, Vol. 2, No. 15, 2006.
- Effect of primary stability on early loaded implants; Štěpánek A., Strnad J., Strnad Z. Clin. Oral. Impl. Res. Vol 16, No. 4, 2005.
- Three-year multicentric study of osseointegrated Impladent implants; Šimůnek A., Štěpánek A., Zábrodský V., Nathanský Z., Strnad Z., Quintessenz, Vol. 6, No. 6, 1997.
- Alkali treatment – new concept of titanium implant surface modification; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Strnad J., Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 15, No. 4, 2004.
Klinische Studien auf Englisch – Kurzfassungen
- Efecto de la altura del pilar en la pérdida ósea periimplantaria; Pico Blanco A.: Universidade de Santiago de Compostela 2021.
- Novák Z, Nesvadba R, Strnad J, Kamprle J, Strnad Z. Marginal bone level and biologic width dynamics in tissue-level and bone-level implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020;31(S20):192. doi:10.1111/clr.134_13644
- Implants with an osteoconductive surface and a moderately rough neck – 3 years of follow-up; Nesvadba R., Novák Z., Strnad J., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(S19):303. doi:10.1111/clr.259_13509
- Stability assessment of immediately loaded alkali-etched implants; Nathanský Z., Strnad J., Strnad Z.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 15, No. 4, 2004.
- Alkali treatment – new concept of titanium implant surface modification; Šimůnek A., Kopecká D., Strnad J.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 15, No. 4, 2004.
- Bioactive titanium implants for shorter healing period; Šimůnek A., Strnad J., Štěpánek A.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 13, No. 4, 2002.
- Peri-implantitis, problems and solutions – a 2 year study; Novák Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 13., No. 6, 2004.
- Use of Impladent dental implants in edentulous jaws; Šimůnek A.: Quintessenz, Vol. 5, No. 5, 1996.
- Three-year multicentric study of osseointegrated Impladent implants; Šimůnek A., Štěpánek A., Zábrodský V., Nathanský Z., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 6, No. 6, 1997.
- Using of dental implants in reconstructive surgery; Holakovský J., Mazánek J., Hubálková H., Nejedlý A., Tvrdek M.: To be published.
Experimentelle Studien auf Englisch
- In Vitro Bioactivity Test of Real Dental Implants According to ISO 23317; Kolafová M., Šťovíček J., Strnad J., Zemek J., Dybal J.: JOMI, Vol. 32, No 6, 2017.
- Alkali–modified Titanium Surface Stimulating Formation of Bone–implant Interface; Strnad J., Macháček J., Strnad Z., Povýšil C., Strnadová M.: Key Engineering Materials, Vols 361-363, pp 749-752, 2008; Bioceramics 20, Nantes, France.
- Secondary Stability Assessment of Titanium Implants with an Alkali-Etched Surface: A Resonance Frequency Analysis Study in Beagle Dogs; Strnad J., Urban K., Povýšil C., Strnad Z., JOMI, Vol. 23, No. 3, 2008.
- Effect of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on the osteoconductivity of commercially pure titanium implants; Strnad Z., Strnad J., Povýšil C., Urban K.: International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, Vol. 15, No. 4, 2000, pp. 483–490.
- Early Interaction of Biomaterials with Dynamic Simulated Body Environment; Strnad J., Strnad Z., Protivínský J., Helebrant A.: in Proc. 5th Asian Symposium on Biomedical Materials (Yasuhiko Tabata ed.), Hong Kong University of Science & Technology, Hong Kong 2001, pp. 51–55.
- The effect of surface roughness and texture on bioactivity of titanium in vitro, in vivo; Strnad Z., Strnad J., Dalibová L.: Transactions of Sixth World Biomaterial Congress, USA, Vol. III, 2000, p. 1055.
- Effect of implant diameter and length on the stress caused in the surrounding bone by the occlusal forces; Himmlová L., Konvičková S., Kácovský A., Dostálová T.: Prakt. Zub. Lék., 48, 2000, pp. 155–163.
- The effect of bioactive surface on implant stability during healing; Strnad J., Urban K., Strnad Z.: Clin. Oral. Impl. Res., Vol. 16, No. 4, 2005.
- Modelling of stress and deformation distribution around endosteal implants; Konvičková S., Kácovský A., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 8, No. 12, 1999.
Experimentelle Studien auf Englisch – Kurzfassungen
- Interaction of acid and alkali treated titanium with dynamic simulated body environment; Strnad J., Protivínský J., Mazur D., Veltruská K., Strnad Z., Helebrant A., Šesták J., J. Therm: Anal. Cal., Vol. 76, 2004, 17–31.
- Chemically treated titanium early surface activity detected in vitro; Strnad J., Protivínský J., Strnad Z., Veselý P.: Clin. Oral impl. Res. Vol. 13, 4, 2002.
- Modelling of stress and deformation distribution around endosteal implants; Konvičková S., Kácovský A., Strnad Z.: Quintessenz, Vol. 8, No. 12, 1999.
- Bone-like apatite formation in titanium and silica glass; Strnad J., Helebrant A., Hamáčková J.: Glass Sci. Techn. – Glastechn.Ber. , Vol. 73, C1, 2000.
- Kinetics of bone-like apatite formation in simulated body fluid; Strnad J., Helebrant A.: in: Proc. 5th ESG Conference (eds. Helebrant A., Kasa S., Maryška M.), pp. B2 9–16, Czech Glass Soc., Praha, 1999.
Quellen zum Graph „Hoher marginaler Knochenerhalt mit Implantaten BioniQ®“
- The Influence of Implant Surface on Maintenance of Marginal Bone Levels for Three Premium Implant Brands: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis; Norton, MR, Astrom, M: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2020;35(6):1099-111.
- Marginal bone response of submerged and non-submerged osteoconductive alkali-etched implants in thick and thin biotypes: A 2-year clinical follow-up study; Novak Z., Strnad J., Nesvadba R., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34(5):1184-1194.
- The influence of biological width violation on marginal bone resorption dynamics around two-stage dental implants with a moderately rough fixture neck: A prospective clinical and radiographic longitudinal study; Strnad J., Novak Z., Nesvadba R., Kamprle J., Strnad Z.: Int J Dent & Ora Hea 2021; 7:6, 20-36.